New research highlights alarming levels of microplastics in the Great Lakes, urging coordinated monitoring and policy changes to address the rising environmental risk.
Microplastics Pollution in Great Lakes Reaches Critical Levels
A new report from the International Joint Commission’s (IJC) Great Lakes Science Advisory Board raises concerns about the widespread presence of microplastics in the Great Lakes. The study highlights that these microscopic plastic particles have permeated the ecosystem, affecting water quality, aquatic life, and possibly human health. With Michigan home to vast portions of these waters, the findings call for immediate policy action and improved monitoring efforts.
Microplastics: An Invisible but Pervasive Threat
Microplastics—plastic fragments less than 5 mm in size—come from industrial sources, synthetic clothing, tire wear, and the breakdown of larger plastics. They have been detected across all five Great Lakes, with Lakes Michigan and Ontario showing the highest concentrations. Alarmingly, the study found that some ambient water samples already exceed ecological risk thresholds, potentially harming fish populations and entering the human food chain.
Dr. Chelsea Rochman, an environmental toxicologist at the University of Toronto and a co-author of the report, emphasizes the growing risks: “We are seeing a clear impact on freshwater species, and the levels of microplastics in drinking water sources are concerning.”
Michigan’s Role in Tackling the Crisis
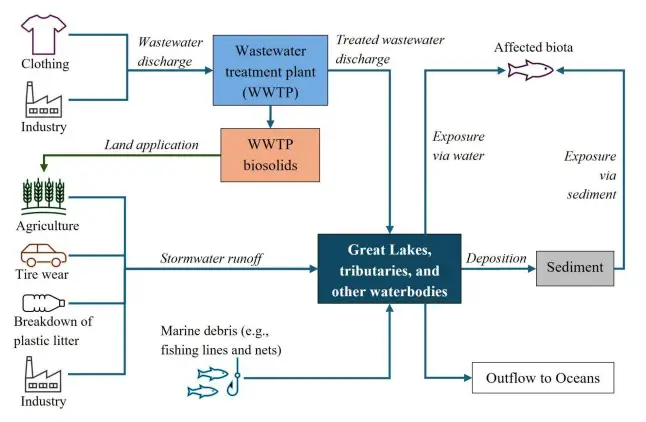
Michigan, as a steward of vast Great Lakes coastlines, is at the forefront of addressing this issue. The IJC report urges the U.S. and Canadian governments to designate microplastics as a Toxic Chemicals sub-indicator under the Great Lakes Water Quality Agreement (GLWQA). Doing so would help establish a coordinated, basin-wide monitoring program, enabling researchers to track trends and pinpoint sources of pollution.
“Without consistent monitoring, we’re flying blind,” says Dr. Rebecca Rooney, an ecologist at the University of Waterloo. “We need a standardized approach to measuring microplastics across the Great Lakes to develop effective mitigation strategies.”
From Research to Action: Policy Recommendations
The report outlines key recommendations:
- Implementing a unified microplastics monitoring system across U.S. and Canadian agencies.
- Adding microplastics to the list of Chemicals of Mutual Concern (CMC) under the GLWQA.
- Developing new policies to prevent microplastic emissions, including stricter regulations on industrial discharge and improved plastic waste management.
Public engagement is also crucial. Experts suggest that Michigan residents can help by reducing plastic use, supporting policy initiatives, and advocating for stronger environmental protections.
A Broader Perspective: Global and Local Solutions
The Great Lakes are not alone in facing microplastic contamination. Countries worldwide are tackling similar crises, with California leading the charge by adopting strict microplastics monitoring laws. Scientists suggest that Michigan could model its response on these efforts, emphasizing community-based cleanups, industry accountability, and research funding.
The study serves as a wake-up call for Michigan policymakers and environmental advocates. Without immediate action, microplastic pollution could pose long-term risks to freshwater ecosystems and public health.
Microplastics Reporting by Thumbwind

Are the Great Lakes a Microplastic Soup With PFAS On the Side? – The next time you brush your teeth or wash your face you may be contributing to adding plastic into the Great Lakes.
Microplastic in Water—4 Critical Areas of Perspective With Our Drinking Water? The study sampled bottled water from various locations around the globe. It pointed out that the cause of contamination was partly the result of plastic packaging and partly the fault of the bottling process. The survey included brands like Nestle, Aquafina, San Pellegrino, Dasani, and Evian.
Michigan Water Filtration – 5 Innovative Solutions for Safety – Michigan Water Filtration systems are more than just hardware; they are a beacon of hope in the aftermath of the Flint Water Crisis. This article delves into the sophisticated technologies that promise safe drinking water across Michigan. Discover how cutting-edge solutions are changing the landscape of water purity in the state.
Find More Interesting Feature Stories From ThumbWind
- Michigan Feature Stories – Unveiling the diverse and vibrant people, captivating places, and remarkable events that make the Great Lake State unique.
- Weird Political News – A sarcastic take on official news from around the U.S., exploring the absurdities in politics with humor.
- Michigan News – Covering local stories, impactful interviews, and updates on community happenings shaping Michigan’s culture.
Your Turn – Like This, or Loath it – We Want to Hear From You
Please offer an insightful and thoughtful comment. We review each response. Follow us to have other feature stories fill up your email box, or check us out on ThumbWind Publications.




